Defending Against Universal Attacks Through Selective Feature Regeneration
-
Tejas Borkar
- Felix Heide
- Lina Karam
CVPR 2020
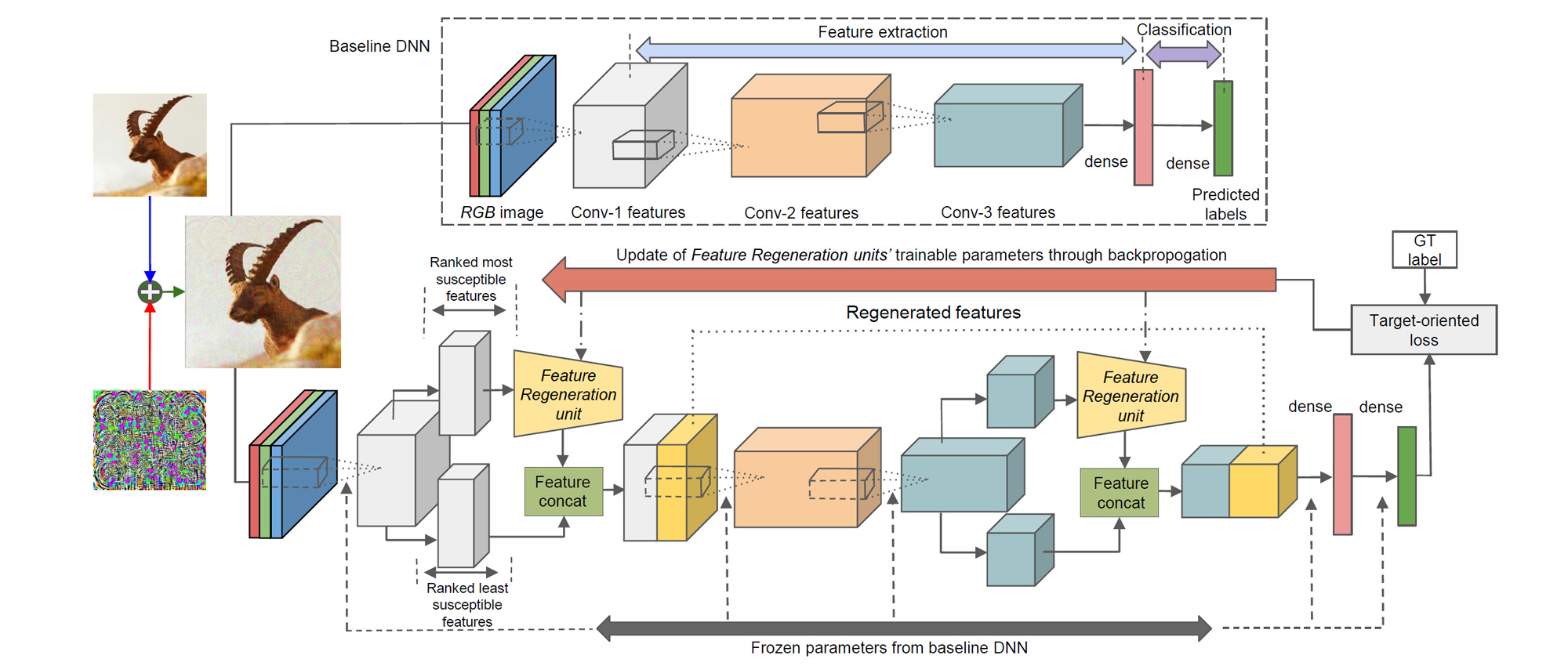
Defending Against Adversarial Attacks by Selective Feature Regeneration: Convolutional filter activations in the baseline DNN (top) are first sorted in order of vulnerability to adversarial noise using their respective filter weight norms (see Manuscript). For each considered layer, we use a feature regeneration unit, consisting of a residual block with a single skip connection (4 layers), to regenerate only the most adversarially susceptible activations into resilient features that restore the lost accuracy of the baseline DNN, while leaving the remaining filter activations unchanged. We train these units on both clean and perturbed images in every mini-batch using the same target loss as the baseline DNN such that all parameters of the baseline DNN are left unchanged during training.
Deep neural network (DNN) predictions have been shown to be vulnerable to carefully crafted adversarial perturbations. Specifically, image-agnostic (universal adversarial) perturbations added to any image can fool a target network into making erroneous predictions. Departing from existing defense strategies that work mostly in the image domain, we present a novel defense which operates in the DNN feature domain and effectively defends against such universal perturbations. Our approach identifies pre-trained convolutional features that are most vulnerable to adversarial noise and deploys trainable feature regeneration units which transform these DNN filter activations into resilient features that are robust to universal perturbations. Regenerating only the top 50% adversarially susceptible activations in at most 6 DNN layers and leaving all remaining DNN activations unchanged, we outperform existing defense strategies across different network architectures by more than 10% in restored accuracy. We show that without any additional modification, our defense trained on ImageNet with one type of universal attack examples effectively defends against other types of unseen universal attacks.
Paper
Tejas Borkar, Felix Heide, Lina Karam
Defending Against Universal Attacks Through Selective Feature Regeneration
CVPR 2020
